What Is the Mediterranean Diet?
The Mediterranean diet is a way of eating that emphasises plant-based foods and healthy fats. It has been widely recognised as one of the healthiest diets for promoting overall well-being, including heart health, weight management, and mental and digestive health.
At the core of the Mediterranean diet are vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, and legumes. These foods provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support optimal health. Olive oil is a primary source of fat in this diet, providing heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and anti-inflammatory properties.
In addition to plant-based foods, the Mediterranean diet includes moderate amounts of cheese and yogurt, both of which are rich in calcium and protein. Fish and poultry are consumed in low to moderate amounts, while red meat is limited. Sweets are enjoyed on special occasions, but not as a regular part of the diet.
By following the Mediterranean diet, you can enjoy a wide variety of flavourful and nutritious meals. From colourful salads with fresh veggies and a drizzle of olive oil, to roasted vegetables with a sprinkle of black pepper and a serving of whole-grain bread, the possibilities are endless.
Overall, the Mediterranean diet is a delicious and sustainable way of eating that provides numerous health benefits, and that can significantly aid in weight loss if that is your goal. Start incorporating the Mediterranean style of eating into your life today and discover the positive impact it can have on your overall well-being!
To help you get started, this article will cover the benefits of the Mediterranean diet, provide insights into how to undertake the diet successfully, and suggest a 2-week meal plan.

Mediterranean Diet Health Benefits
The Mediterranean diet offers numerous health benefits due to its emphasis on plant-based foods and healthy fats. One of the key advantages of this diet is its anti-inflammatory properties. By consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts, individuals can reduce inflammation in the body, which is linked to various chronic diseases.
Moreover, the Mediterranean diet has been consistently associated with improved heart health. Studies have shown that following this eating pattern can help maintain healthy cholesterol and blood pressure levels, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
In addition to its positive impact on heart health, the Mediterranean diet has also been linked to improved brain function. The abundance of nutrient-rich foods, such as fatty fish, olive oil, and nuts, provide essential nutrients that support cognitive health and help protect against age-related cognitive decline.
Furthermore, following a Mediterranean diet has been associated with increased longevity. The combination of a plant-based diet, healthy fats, and moderate consumption of meat and dairy products provides a balanced approach to nutrition that promotes overall well-being.
Perhaps most notably for individuals with weight loss goals, the Mediterranean diet is widely considered to be one of the most effective diet plans.
Mediterranean Diet Foods List
By incorporating the following foods into your daily meals, you will set yourself up for success on the Mediterranean diet, in addition to promoting overall well-being and improving your health.
Protein
Protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining and repairing our body’s tissues. In the context of the Mediterranean Diet, there are various sources of protein that can be incorporated into your daily meals.
Plant-based protein sources are highly encouraged in the Mediterranean diet, and options such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas are very popular. These legumes are not only rich in protein but also provide a good amount of fibre, which promotes digestive health. Additionally, tofu, tempeh, and seitan are great options for those who prefer a vegetarian or vegan approach.
When it comes to animal-based protein, the Mediterranean diet recommends consuming chicken, fish, seafood, and eggs occasionally. Poultry, like chicken, is a lean source of protein that can be prepared in various ways, adding versatility to your meal plan. Fish and seafood, particularly fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are great sources of omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health.
However, it is important to note that red meat, cured meats, and processed meat products should be limited or avoided altogether. These meats are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other health issues, so it’s best to opt for leaner protein choices.
By incorporating these protein sources into your Mediterranean diet, you can enjoy a well-rounded and balanced approach to nutrition, promoting overall health and well-being.
Oil and Fat
Oil and fat play a critical role in the Mediterranean diet, providing flavour, texture, and essential nutrients. However, it is important to choose healthy fat sources and consume them in moderation.
In the Mediterranean diet, the primary fat source is olive oil. This golden elixir is rich in monounsaturated fats, which are known to support heart health. It is recommended that you use olive oil as the main cooking oil and as a drizzle over dishes like salads, roasted vegetables, or grain bowls.
Consumption guidelines for oil and fat in the Mediterranean diet suggest limiting saturated and trans fats, commonly found in sources like butter, margarine, and processed snacks. Instead, focus on healthier options like olive oil.
When incorporating oil and fat into your meals, it is important to practice portion control. Be mindful of the amount you use while cooking, baking, or dressing your dishes. Just a small amount can go a long way in adding flavour and providing necessary nutrients.
By opting for healthy fat sources like olive oil and avoiding excessive fat intake, you can reap the potential benefits for your heart health while enjoying the delicious flavours of the Mediterranean diet.
Fruits and Veggies
One of the key components of the Mediterranean diet is the abundance of fruits and vegetables. This eating plan encourages the consumption of a wide variety of colourful produce, both non-starchy and starchy vegetables, as well as all types of fruits.
Non-starchy vegetables commonly enjoyed in the Mediterranean diet include zucchini, bell peppers, artichokes, broccoli, and spinach. These vegetables are low in calories and high in fibre, vitamins, and minerals, making them an excellent choice for maintaining a healthy weight and promoting digestive health.
In addition to non-starchy vegetables, starchy vegetables are also part of the Mediterranean diet. Sweet potatoes, carrots, beets, and other root vegetables provide valuable complex carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals to support optimal health.
When it comes to fruits, all varieties are allowed in the Mediterranean diet. Whether it’s peaches, cherries, strawberries, or blueberries, fruits are a delicious and nutritious way to satisfy your sweet tooth while providing essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
One of the great things about the Mediterranean diet is that no fruits or vegetables are off-limits. This flexibility allows for a wide variety of flavours and nutrients to be incorporated into your meals, making it easier to stick to this healthy eating plan. So go ahead and enjoy the vibrant array of fruits and vegetables that the Mediterranean diet has to offer!
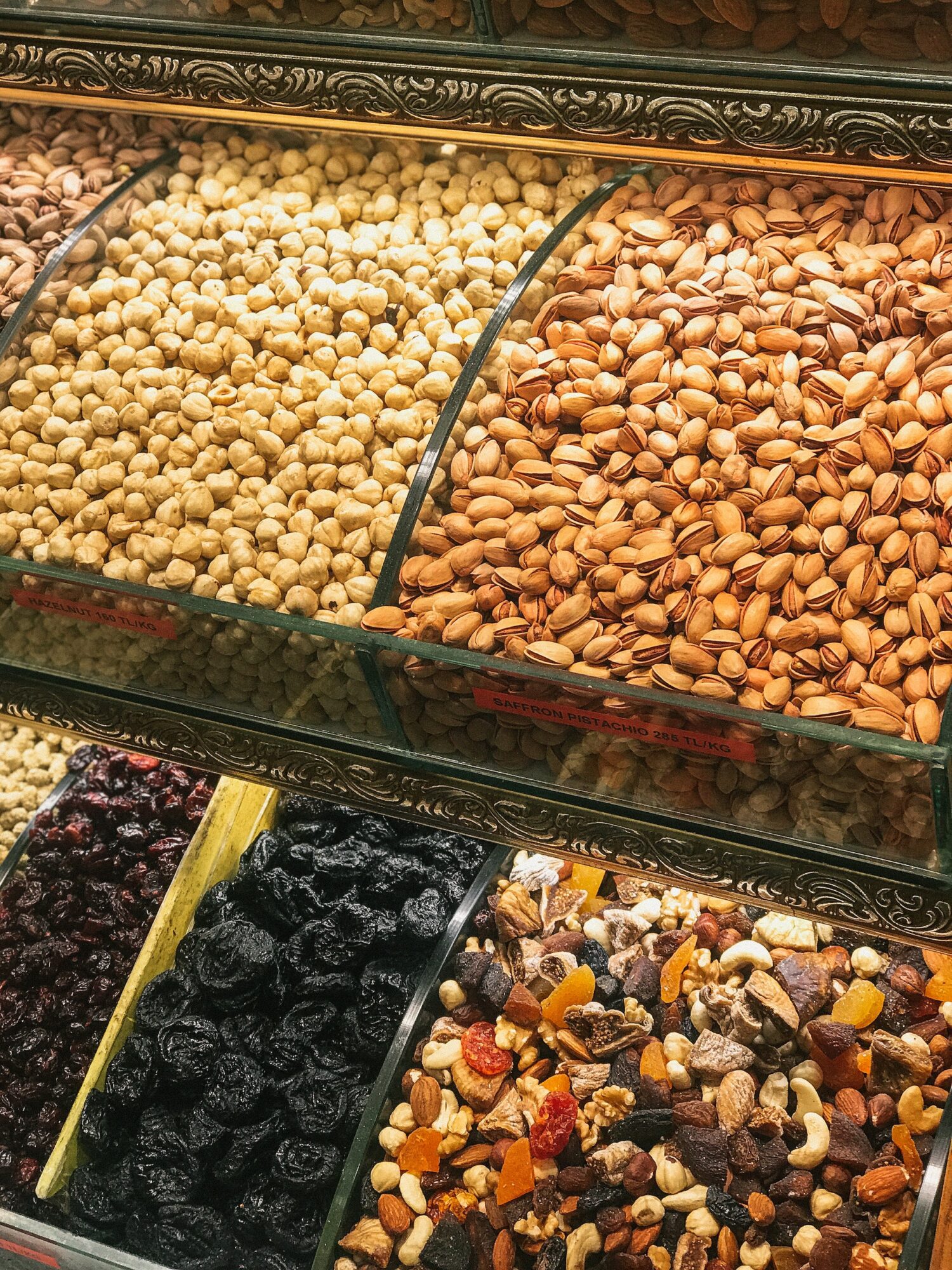

Nuts and Seeds
Nuts and seeds are an essential component of a Mediterranean diet meal plan, offering a plethora of health benefits. Rich in heart-healthy fats, nuts such as walnuts, almonds, and pistachios can help improve cardiovascular health. These heart-healthy polyunsaturated fats have been shown to lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
In addition to their cardiovascular benefits, including nuts and seeds in your diet can also support digestive health. They are a great source of dietary fibre, which promotes regular bowel movements and aids in maintaining a healthy gut microbiome.
A variety of nuts and seeds can be included in your Mediterranean diet meal plan. Almonds, walnuts, pistachios, cashews, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and pumpkin seeds are just a few examples.
Remember to enjoy nuts and seeds in moderation, as they are high in calories. We recommend aiming for a handful per day.
Grains
Grains are a staple in the Mediterranean diet, providing a rich source of fibre, vitamins, and minerals. Included in this healthy eating pattern are various types of grains, each offering its own unique nutritional profile to support overall well-being.
Whole-grain bread is a popular choice and a key component of the Mediterranean diet. When selecting whole-grain bread, it is important to ensure that whole-wheat flour is listed as the first ingredient. This ensures that you are getting the maximum nutritional benefits from the grain.
Other notable grains commonly found in Mediterranean cuisine include farro, bulgur wheat, barley, and quinoa. These grains offer a pleasing nutty flavour and a delightful texture to meals. Farro, in particular, is known for its high protein content, while bulgur wheat contains significant amounts of fibre.
Additionally, there are a variety of other grain options to choose from to add diversity to your meals. These include pasta, couscous, whole-grain crackers, and polenta. While the Mediterranean diet primarily focuses on whole grains, it also allows for occasional inclusion of these refined grain options.
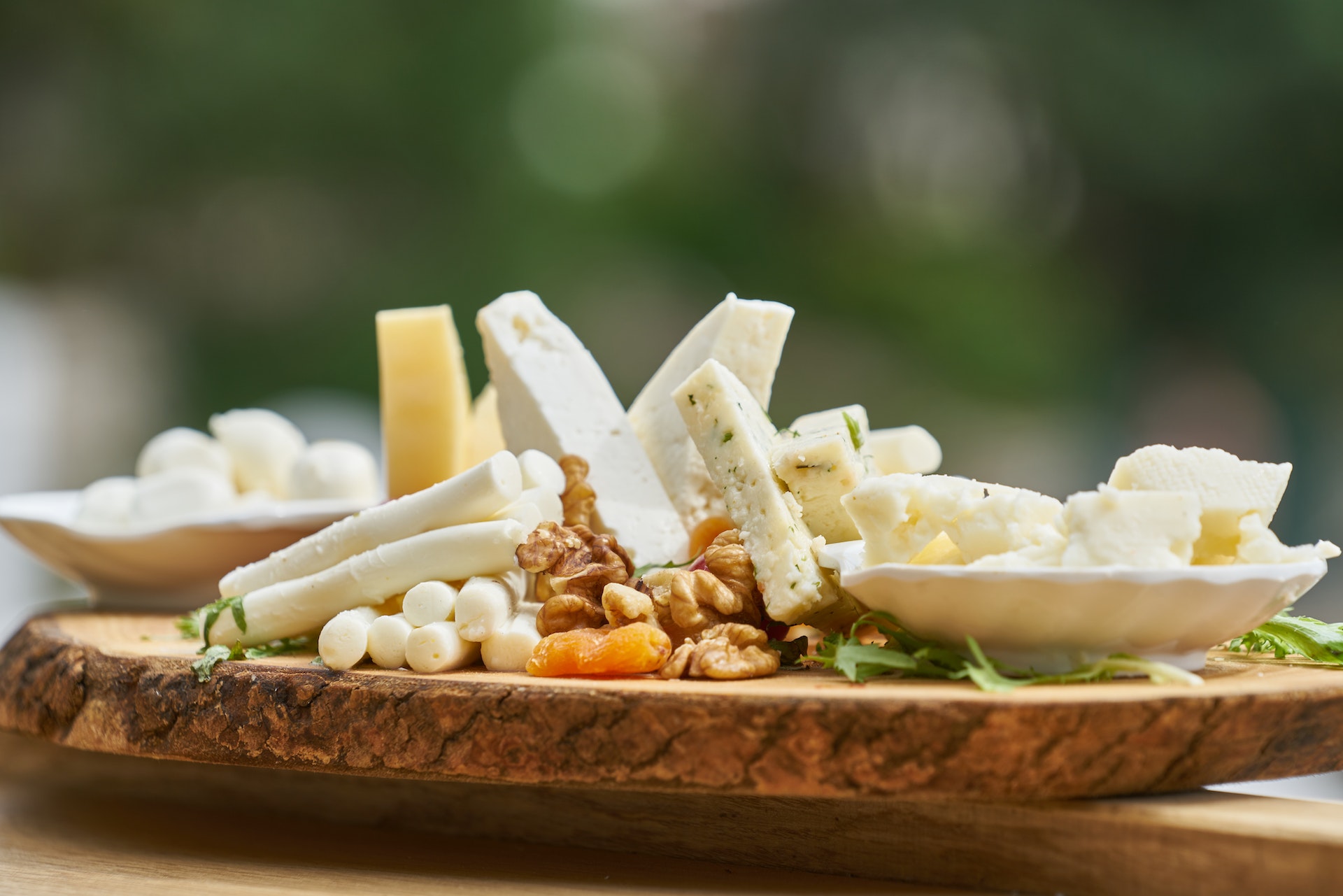

Dairy
Dairy is an integral part of the Mediterranean diet, although it should be consumed in moderation. The Mediterranean diet emphasises whole, unprocessed foods, and dairy products can provide important nutrients like calcium and protein. When incorporating dairy into your Mediterranean meal plan, it is important to choose products that are minimally processed and low in added sugars.
Plain Greek yogurt is an excellent choice, as it is rich in protein and probiotics that contribute to a healthy digestive system. Other recommended dairy options include ricotta and cottage cheese, both of which are versatile and can be used in a variety of Mediterranean recipes.
When it comes to cheese, opt for varieties like Brie, feta, or goat cheese, which are lower in saturated fat compared to other types. These cheeses add flavour to Mediterranean dishes without overpowering them.
On the other hand, there are dairy products that should be avoided or consumed rarely in the Mediterranean diet. This includes ice cream, which is typically high in added sugars and unhealthy fats. Sweetened yogurt and processed cheeses should also be limited, as they can contain added sugars, preservatives, and unhealthy oils.
Sweeteners
In the Mediterranean diet, sweeteners should be consumed in moderation. While it’s important to limit added sugars, there are still options available to satisfy your sweet tooth. Honey is a popular choice and a natural sweetener that can be used in moderation. Its distinct flavour adds a touch of sweetness to dishes like yogurt or oatmeal.
Small amounts of added sugar can also be used sparingly. However, it’s important to be mindful of the quantity and choose healthier alternatives whenever possible.
When it comes to snacks, there are plenty of healthy options that align with the Mediterranean diet. For a quick and satisfying treat, try fresh fruit paired with a drizzle of honey or a sprinkle of cinnamon. This combination provides natural sweetness without the need for added sugars. Greek yogurt topped with sliced almonds and a drizzle of honey is another delicious choice.
Remember, the key to a successful Mediterranean diet is balance and moderation. Enjoying sweeteners in small amounts can contribute to a well-rounded and enjoyable eating plan.

Condiments and Sauces
One of the great things about the Mediterranean diet is that it allows for the use of a variety of flavourful condiments and sauces to enhance the taste of meals. When it comes to condiments and sauces, there are different types that can be included in the Mediterranean diet, each with its own guidelines.
Tomato sauce, especially when it is made without added sugar, is a staple in Mediterranean cooking and can be used liberally. Its rich flavour and versatility make it a great choice for pasta dishes or as a base for soups and stews.
Pesto, made with ingredients like basil, garlic, pine nuts, and olive oil, is another condiment that can be used generously in the Mediterranean diet. Its fresh and vibrant taste adds depth to meals, whether it’s mixed in with pasta or used as a spread on sandwiches.
Balsamic vinegar is a tangy and slightly sweet condiment that can also be used liberally in the Mediterranean diet. It adds a burst of flavour to salads, roasted vegetables, and even grilled meats or fish.
There are some condiments that should be used more sparingly in the Mediterranean diet. Aioli, a creamy sauce made with garlic and olive oil, can be included occasionally. Tahini, a paste made from ground sesame seeds, and tzatziki, a yogurt and cucumber sauce, are also condiments that can be enjoyed in moderation.
On the other hand, condiments like barbecue sauce, ketchup, and teriyaki sauce should be used rarely or avoided altogether in the Mediterranean diet due to their high sugar and sodium content.
By incorporating these flavourful condiments and sauces into your Mediterranean-style meals, you can continue to enjoy a variety of tastes while still maintaining a healthy and balanced diet.
Drinks
Drinks play an important role in the Mediterranean diet, as they can greatly impact our overall health and well-being. When it comes to beverages, the Mediterranean diet encourages some choices while discouraging others.
First and foremost, water is the number one recommended beverage in the Mediterranean diet. Staying hydrated is essential for good health, and water is the perfect choice to quench your thirst throughout the day.
Coffee and tea are also widely enjoyed in the Mediterranean diet. These beverages can be consumed liberally, as long as you are mindful of any added sugars or creams. Black coffee and unsweetened herbal teas are particularly beneficial and can contribute to your hydration goals.
When it comes to alcohol, red wine is often associated with the Mediterranean diet. However, it’s important to note that alcohol consumption should be moderate and reserved for special occasions. A glass of red wine can be enjoyed occasionally, as it has been linked to potential health benefits such as heart health.
On the other hand, there are beverages that should be consumed rarely or not at all in the Mediterranean diet. Sodas, fruit juices, and bottled sweetened coffee drinks are high in added sugars and can have negative effects on your health. It is best to limit or avoid these sugary beverages altogether.
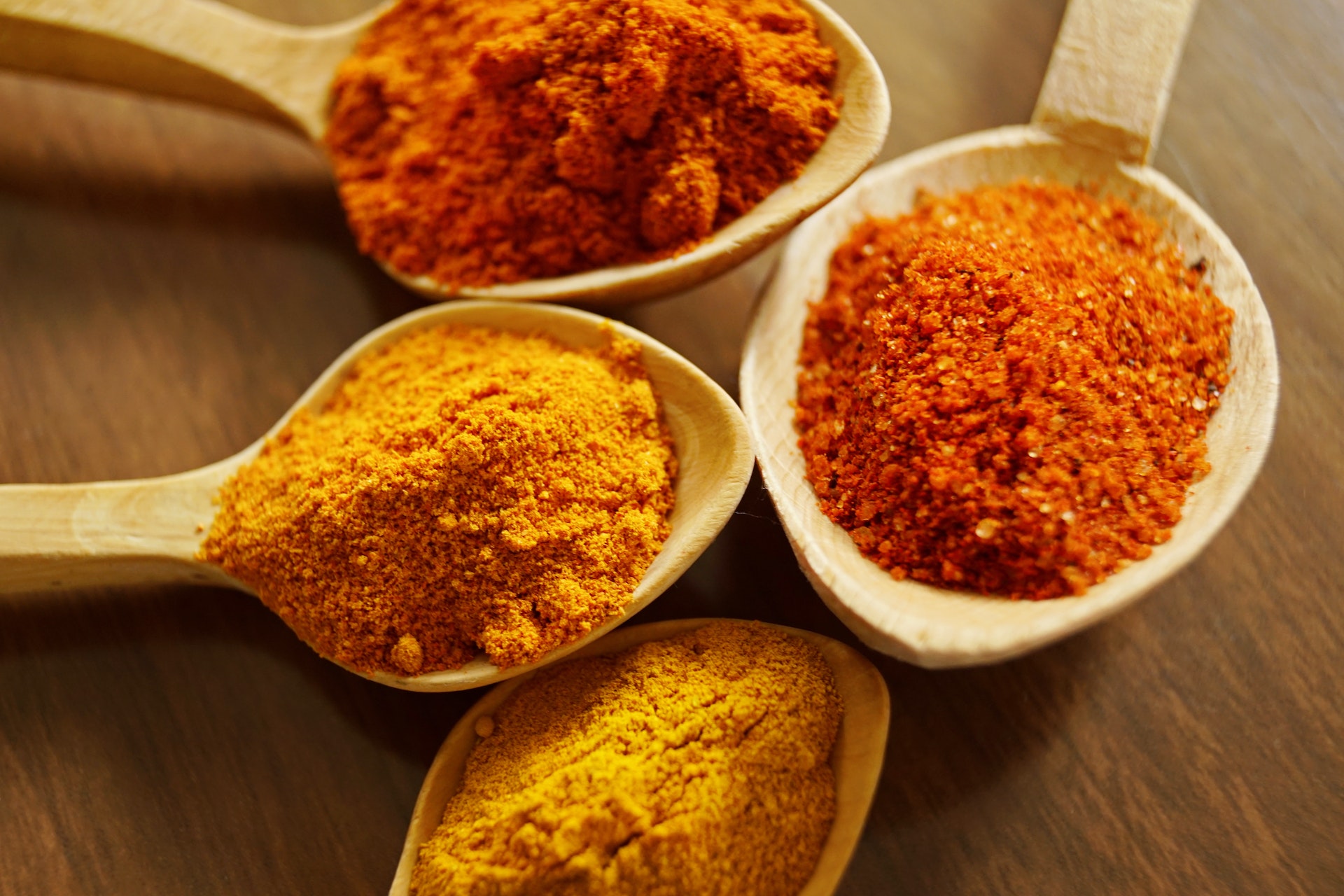

Herbs and Spices
One of the key characteristics of the Mediterranean diet is its abundant use of herbs and spices. These additions not only enhance the taste of dishes, but also offer numerous health benefits.
In Mediterranean cuisine, herbs such as oregano, basil, thyme, and rosemary are commonly used. Oregano, in particular, is rich in antioxidants and has antimicrobial properties. Basil is known for its anti-inflammatory benefits, while thyme has been linked to improved respiratory health. Rosemary is believed to support digestion and brain health.
Spices like cinnamon, cumin, and turmeric are also popular in Mediterranean cooking. Cinnamon can help regulate blood sugar levels and has anti-inflammatory properties. Cumin aids in digestion and may help with weight management. Turmeric, known for its vibrant yellow colour, contains the compound curcumin which has been studied for its potential anti-cancer properties.
In the Mediterranean diet, herbs and spices can be used liberally. There are no restrictions on their use, and individuals are encouraged to salt their food to taste. However, some spices such as saffron can be expensive and are often reserved for special occasions. Similarly, certain herbs like dill or fenugreek may be used less frequently in Mediterranean dishes.
Your 14-Day Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet
In this 14-day meal plan, we provide you with a variety of delicious and nourishing recipes that incorporate the key components of the Mediterranean diet. From hearty salads and comforting stews to flavourful grilled dishes and satisfying snacks, this meal plan will help you enjoy the rich flavours of this part of the world while nourishing your body and promoting overall well-being. Let’s start your Mediterranean journey!
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 1
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt with honey, walnuts, and fresh berries (250 kcal)
- Lunch: Lentil soup with whole grain bread and a mixed salad (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Grilled chicken with roasted vegetables (zucchini, bell pepper, and eggplant) and quinoa (550 kcal)
- Snack: Hummus with carrot and cucumber sticks (150 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 2
- Breakfast: Whole grain toast with avocado and poached egg. A side of mixed fruits (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Tuna salad with olives, tomatoes, and feta cheese (450 kcal)
- Dinner: Whole grain spaghetti with a tomato, basil, and garlic sauce (500 kcal)
- Snack: A handful of almonds and a piece of dark chocolate (200 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 3
- Breakfast: Oatmeal with sliced almonds, dried figs, and a drizzle of honey (250 kcal)
- Lunch: Chickpea and vegetable stir-fry with lemon-tahini dressing (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Baked salmon with a side of steamed asparagus and couscous (500 kcal)
- Snack: Greek yogurt with a drizzle of honey (150 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 4
- Breakfast: Whole grain waffles with fresh berries and a drizzle of honey (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Vegetable and feta stuffed bell peppers (350 kcal)
- Dinner: Lamb kebabs with tzatziki sauce and a mixed green salad (600 kcal)
- Snack: Sliced apple with a spoon of almond butter (150 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 5
- Breakfast: Shakshuka (poached eggs in a spicy tomato and vegetable sauce) (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Spinach and ricotta stuffed whole grain crepes (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Grilled shrimp with garlic and lemon, side of tabbouleh salad (500 kcal)
- Snack: Mixed olives and feta cheese (200 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 6
- Breakfast: Fresh fruit salad with a sprinkle of chia seeds and a glass of almond milk (250 kcal)
- Lunch: Tomato and mozzarella salad with basil and balsamic glaze (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Vegetable paella with saffron and artichokes (500 kcal)
- Snack: Handful of pistachios (150 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 7
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs with spinach, tomatoes, and olives (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Grilled aubergine and hummus wrap with a side of Greek salad (450 kcal)
- Dinner: Cod fillet with a lemon and herb dressing, side of roasted broccoli (500 kcal)
- Snack: Fresh figs (150 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 8
- Breakfast: Smoothie with banana, spinach, Greek yogurt, and a sprinkle of flaxseeds (250 kcal)
- Lunch: Chicken and vegetable skewers with a side of quinoa salad (450 kcal)
- Dinner: Whole grain risotto with mushrooms and Parmesan (550 kcal)
- Snack: Sliced cucumber with tzatziki dip (100 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 9
- Breakfast: Whole grain toast with ricotta, honey, and sliced strawberries (280 kcal)
- Lunch: Lentil and vegetable salad with a lemon-olive oil dressing (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Grilled steak with a side of Mediterranean potato salad (550 kcal)
- Snack: A piece of dark chocolate with a handful of walnuts (200 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 10
- Breakfast: Muesli with almond milk, dried apricots, and nuts (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Falafel wrap with lettuce, tomatoes, and tahini sauce (450 kcal)
- Dinner: Baked trout with herbs, lemon, and a side of steamed green beans (500 kcal)
- Snack: Mixed berries (100 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 11
- Breakfast: Frittata with zucchini, tomatoes, and feta cheese (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Spinach and chickpea stew with a side of whole grain bread (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Chicken tagine with olives and preserved lemon, side of couscous (600 kcal)
- Snack: Sliced melon (100 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 12
- Breakfast: Pancakes with almond butter, honey, and sliced bananas (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Mozzarella, tomato, and basil panini with a mixed salad (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Seared tuna steak with a side of roasted Mediterranean vegetables (550 kcal)
- Snack: Carrot sticks with hummus (150 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 13
- Breakfast: Smoothie bowl with Greek yogurt, mixed fruits, and granola (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Quinoa and roasted vegetable salad with a pesto dressing (400 kcal)
- Dinner: Lamb stew with tomatoes, olives, and rosemary (550 kcal)
- Snack: A piece of baklava (200 kcal)
Meal Plan: Mediterranean Diet | Day 14
- Breakfast: Omelette with mushrooms, spinach, and olives (300 kcal)
- Lunch: Tomato and lentil soup with a sprinkle of feta cheese (350 kcal)
- Dinner: Grilled sardines with a lemon and herb marinade, side of garlic sautéed spinach (550 kcal)
- Snack: Fresh pomegranate seeds (150 kcal)
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Mediterranean diet is not just a trend or a temporary fad, but a lifestyle that promotes overall health and well-being. Its emphasis on fresh, whole foods, and the avoidance of processed and unhealthy ingredients, make it a sustainable and effective way of eating.
The Mediterranean diet has been extensively studied and shown to have numerous benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. It is not only a delicious and enjoyable way to eat, but also a practical and achievable dietary approach for people of all ages and backgrounds. By embracing the principles of the Mediterranean diet, individuals can improve their quality of life and experience long-term health benefits.