Hypertension crisis is a medical emergency that occurs when your blood pressure increases sharply to dangerous levels. It is simply a more severe form of hypertension.
Hypertensive crisis is divided into two categories: hypertensive urgency and hypertensive emergency. This article aims to provide patients with an understanding of hypertensive crisis, including its causes, symptoms, and management strategies to handle this life-threatening situation effectively.
Hypertension: Crisis Point or Not?
As mentioned previously, hypertensive crisis can be divided into 2 categories:
- Hypertensive Urgency: This category is marked by a significant elevation in blood pressure without any signs of organ damage. Blood pressure readings typically exceed 180/120 mm Hg. Patients may not experience any symptoms at this stage, making it difficult for them to identify the crisis.
- Hypertensive Emergency: The more severe form of hypertension crisis, hypertensive emergency, is characterised by blood pressure exceeding 180/120 mm Hg, coupled with evidence of end-organ damage, such as in the brain, heart, kidneys or lungs. In this situation, patients are more likely to experience noticeable symptoms and require immediate medical intervention.
Causes of Hypertension Crisis
Multiple factors can contribute to a hypertension crisis, including:
- Inadequate blood pressure management: Failing to take prescribed medications or following the recommended treatment plans may lead to a dangerous rise in blood pressure levels.
- Medications and drug interactions: Consuming certain over-the-counter medications, such as decongestants, or taking illicit drugs like cocaine and amphetamines could trigger a hypertensive crisis.
- Existing medical conditions: Kidney disease, heart failure, and some endocrine disorders like pheochromocytoma can predispose patients to hypertensive crises.
- Sudden withdrawal from medications: Discontinuing certain medications, such as beta-blockers and clonidine, without proper tapering might cause a sharp increase in blood pressure.
Hypertension Crisis Symptoms
Patients experiencing a hypertensive emergency may display various symptoms, including:
- Severe headache
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness and blurred vision
- Confusion, memory loss, or seizures
- Swelling or oedema
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms.

Hypertension Crisis: Treatment
A combination of proper medical care and self-management is essential in handling a hypertensive crisis. The following steps outline the process:
- Medical care: If you suspect a hypertensive emergency, visit a doctor or hospital immediately. Medical staff will administer appropriate intravenous medications to rapidly lower your blood pressure. In hypertensive urgencies, oral medications may suffice to gradually reduce blood pressure over a short period.
- Blood pressure monitoring: Regular blood pressure measurements are crucial for patients at risk of or experiencing hypertensive crises. Invest in an accurate at-home blood pressure monitor to track your readings and report any significant changes to your healthcare provider.
- Medication adherence: It is essential to follow your doctor’s recommendations regarding medications and not to skip or discontinue any without proper consultation.
- Lifestyle modifications: Healthy lifestyle choices can significantly contribute to blood pressure control. These include a balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
- Follow-up care: Regular visits to your healthcare provider will help assess your treatment’s effectiveness and optimise your blood pressure management.
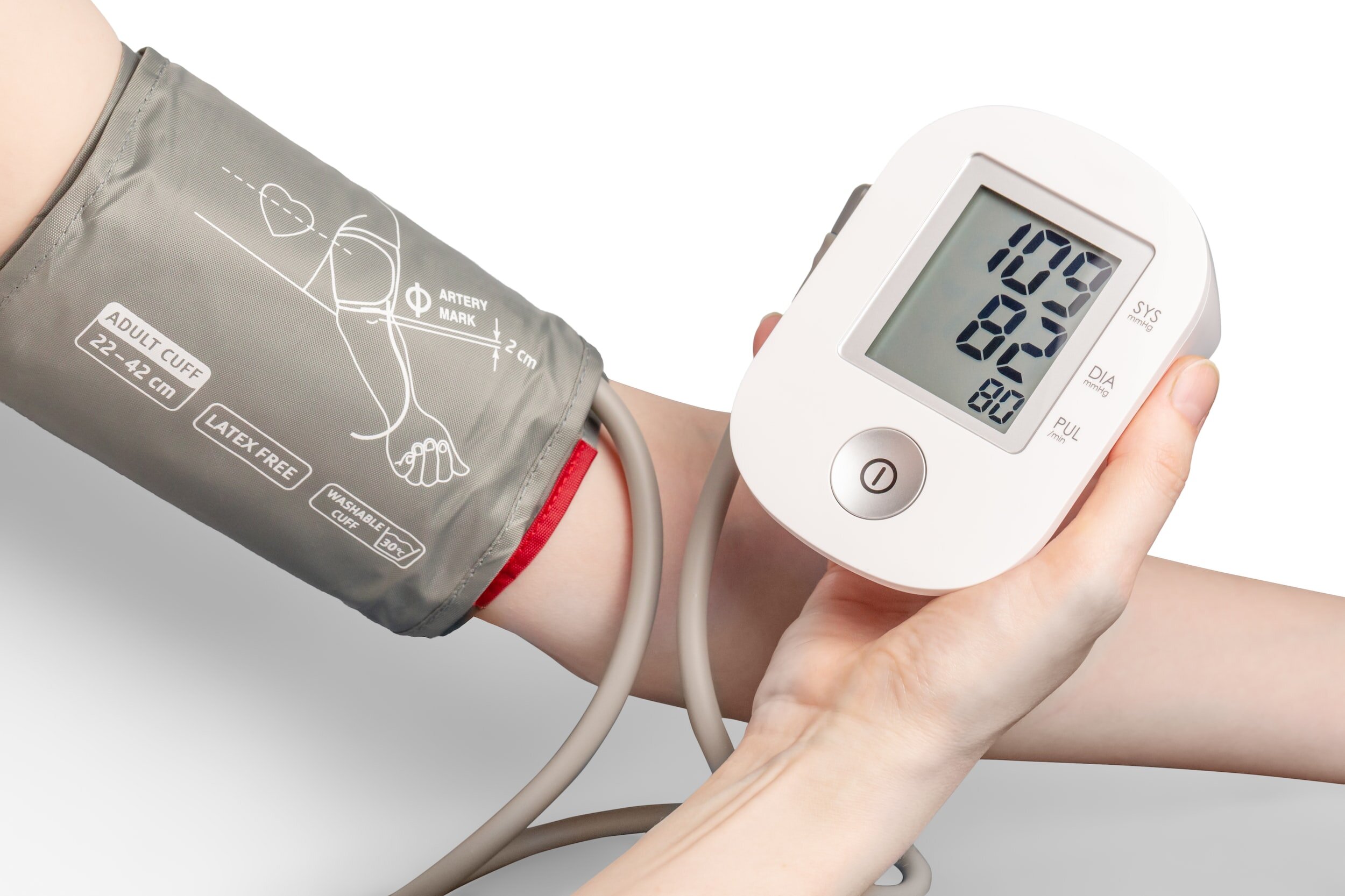
How to Take Your Blood Pressure at Home
The most ideal time to measure your blood pressure is when you are relaxed. For many people, this is impossible in healthcare settings. For an accurate idea about how well your blood pressure is controlled, take regular blood pressure readings at home and keep a log. Sharing this with your doctor can be an invaluable way to ensure that you are getting the right treatment.
To ensure accurate readings, follow these steps:
- First, choose an appropriate blood pressure monitor, ideally one with a digital display and an upper-arm cuff. An example of a blood pressure cuff meeting these specifications can be found here: Blood Pressure Monitor (CE Approved)
- Ensure the cuff size is suitable for your arm, as an incorrect size can affect the readings.
- Before taking your blood pressure, make sure to relax and avoid caffeine, tobacco, or exercise for at least 30 minutes prior.
- Find a quiet space and sit upright in a comfortable chair, with your back supported and your feet flat on the ground.
- Rest your arm on a flat surface, with your palm facing up and ensuring that the middle of the upper arm cuff is at the level of your heart.
- Put the cuff on your bare skin, not over clothing, and ensure it is snug but not too tight.
- Press the start button on the monitor and remain still and silent throughout the measurement, as talking or moving can result in inaccurate readings.
After the measurement is complete, the monitor will display your systolic and diastolic blood pressures. To maintain accuracy, take two or three readings – waiting a few minutes between each – and calculate an average. By consistently following these guidelines, you can support your blood pressure management and gain valuable insights into your overall health.
Conclusion
Understanding hypertensive crisis and its potential risks empowers patients to take appropriate actions when faced with such a situation. By being vigilant of the symptoms, adhering to prescribed treatments, and practising healthy lifestyle habits, patients can mitigate the risks of hypertensive crisis and ensure better overall health.
Please note: If you purchase products by clicking on links on this page, The Check Up may earn a small commission.