What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is a measurement of the pressure of the blood in your arteries. It is measured in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) and typically consists of two numbers: systolic pressure over diastolic pressure.
The systolic pressure represents the force exerted on the arteries when the heart contracts, while the diastolic pressure represents the force when the heart is at rest between beats. The higher number is the systolic pressure, and the lower number is the diastolic pressure.
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is crucial for overall well-being as high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular diseases. Proper monitoring, regular physical activity, and a balanced diet can help manage and maintain blood pressure within a healthy range. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate blood pressure readings and to discuss any concerns or treatment options.
Normal Blood Pressure: Men & Women
Many people wonder if what is considered “normal” blood pressure of a man is different from a woman. The reality is that the normal range for blood pressure is consistent in adults, for both men and women. According to the American Heart Association (AHA), a normal blood pressure reading is below 120/80 mmHg (which applies to men and women).
However, for men, the upper limit is slightly higher at 129/79 mmHg. This means that a man can have a slightly higher reading than a woman and still be considered normal.
When it comes to hypertension, men are more likely than women to have higher readings. According to a study published in the American Heart Journal, 32% of men and 28% of women aged 45–64 years had high blood pressure. Additionally, the prevalence of hypertension increases with age for both genders but tends to be higher in men than in women.
Blood Pressure Categories
When assessing whether your blood pressure is healthy, it’s essential to understand the different blood pressure categories. These include:
1. Elevated blood pressure: Systolic pressure between 120-129 mmHg and diastolic pressure below 80 mmHg.
2. Hypertension stage 1: Systolic pressure between 130-139 mmHg or diastolic pressure between 80-89 mmHg.
3. Hypertension stage 2: Systolic pressure 140 mmHg or higher, or diastolic pressure 90 mmHg or higher.
4. Hypertensive crisis: Systolic pressure higher than 180 mmHg and/or diastolic pressure higher than 120 mmHg.
In recent updates, the AHA has lowered the threshold for high blood pressure. Previously, a reading of 140/90 mmHg or above was considered hypertensive, but now a reading of 130/80 mmHg or above is classified as hypertension stage 1.
It is important to note that blood pressure readings can be influenced by various factors, including physical activity, stress, and underlying health conditions. Regular monitoring of blood pressure, through accurate measurement with a blood pressure monitor and consultation with a healthcare provider, is crucial in managing cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart disease and other associated conditions.
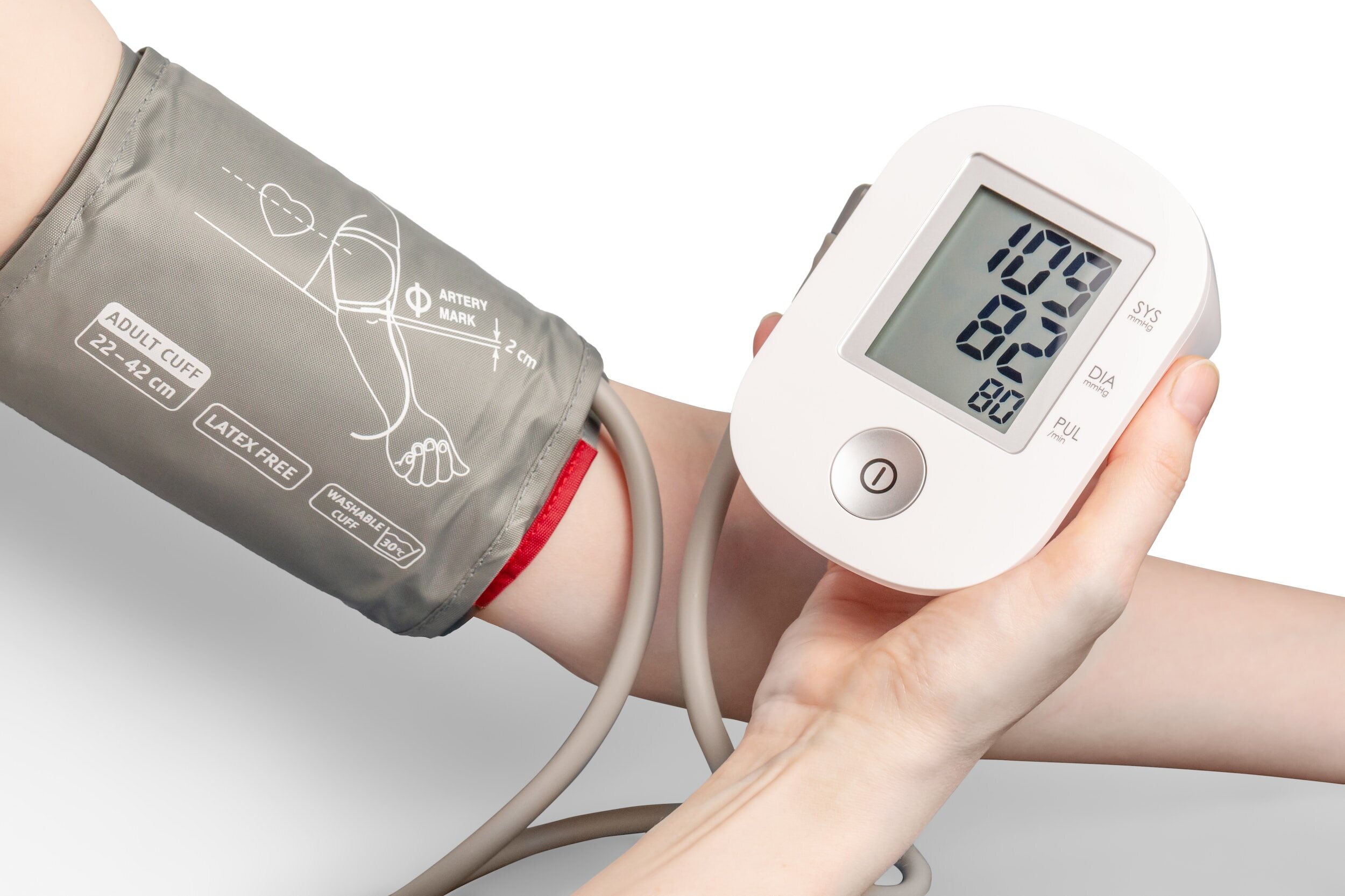
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it often shows no symptoms until it becomes severe. However, there are certain signs and symptoms that may be present in some individuals.
These can include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Nosebleeds
It’s important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to high blood pressure and can be caused by other factors as well.
Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath is a symptom commonly associated with high blood pressure. When blood pressure is elevated, it can cause the heart to work harder to pump blood through the arteries. This increased workload on the heart can lead to inadequate blood flow to major organs, including the lungs.
When there is a decrease in blood flow to the lungs, it can result in difficulty breathing. Those who experience shortness of breath as a symptom of high blood pressure may feel like they are unable to take a deep breath or that they are not getting enough air. This can be accompanied by a feeling of tightness in the chest or a sensation of being suffocated.
Low blood pressure can also lead to inadequate blood flow to major organs, giving rise to shortness of breath. When blood pressure drops too low, blood flow to the lungs may be compromised, causing difficulty breathing. This can occur in people with certain health conditions or as a side effect of certain medications.
Experiencing shortness of breath is a warning sign that should not be ignored. It can be a sign of a serious underlying medical condition, such as cardiovascular disease or heart failure. If you are experiencing persistent shortness of breath, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Remember, timely diagnosis and management of high or low blood pressure can help prevent complications and improve overall health and quality of life.
Dizziness or Headaches
Dizziness and headaches are common symptoms that may be associated with high blood pressure. When blood pressure levels are elevated, it can cause the blood vessels to narrow, restricting the flow of blood and oxygen to the brain. This inadequate blood flow can lead to dizziness and lightheadedness, making it difficult for men and women to maintain their balance and feel steady on their feet.
Headaches, particularly ones that occur in the back of the head and neck, can also be a sign of high blood pressure. The increased pressure in the blood vessels can lead to tension and discomfort, resulting in headaches that may range from mild to severe.
These symptoms of dizziness and headaches should not be taken lightly, as they can indicate potential dangers. High blood pressure is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. It is essential for men and women experiencing these symptoms to monitor their blood pressure regularly and consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.

Chest Pain
Chest pain can be a concerning symptom that is sometimes associated with high blood pressure. The increased pressure in the arteries can lead to inflammation and damage to the walls of the blood vessels, including those supplying the heart muscle. This can eventually result in the development of heart disease.
When high blood pressure contributes to heart disease, it can increase the risk of a heart attack. The additional strain on the arteries restricts blood flow to the heart, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients. This can cause chest pain, also known as angina, as the heart muscle is deprived of its necessary blood supply.
Symptoms of chest pain that may be associated with high blood pressure include a feeling of tightness or pressure in the chest, discomfort that radiates down the arm or to the jaw, shortness of breath, nausea, and sweating. It is important to note that not all chest pain is linked to high blood pressure, as there can be other causes such as heartburn or muscle strain. However, if you experience persistent or severe chest pain, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Fatigue or Confusion
Fatigue and confusion are potential symptoms that may be associated with high blood pressure. These symptoms can often be overlooked or attributed to other causes, making it important to recognise them as potential indicators of elevated blood pressure.
High blood pressure can contribute to fatigue and confusion by reducing blood flow to the brain. When blood pressure is high, it puts strain on the arteries, causing them to become narrow and restricting the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the brain. This reduced blood flow can result in symptoms such as feeling tired or lacking energy, as well as experiencing difficulty concentrating or thinking clearly.
It is crucial to be aware that fatigue or confusion can be signs of high blood pressure and not dismiss them as simply being a result of a busy or stressful lifestyle. If you experience persistent or unexplained fatigue or confusion, it is important to monitor your blood pressure and consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
In addition to elevated blood pressure, other factors such as certain medications, sleep disorders, and underlying health conditions can also contribute to fatigue or confusion. Therefore, it is essential to have a comprehensive evaluation to identify the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
By recognising fatigue and confusion as potential symptoms of high blood pressure in men and women, individuals can take proactive steps to monitor their blood pressure, adopt a healthy lifestyle, and seek medical attention when necessary to prevent potential complications associated with cardiovascular disease.
Causes of High Blood Pressure in Men and Women
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a common health condition that affects many men and women. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the arteries is too high, putting strain on the cardiovascular system. There are several factors that can contribute to high blood pressure in men and women.
Firstly, age plays a role, as blood pressure tends to increase with age. In addition, lifestyle choices such as a poor diet, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption can also lead to high blood pressure.
Other risk factors include family history, obesity, smoking, and certain medical conditions, such as chronic kidney disease and sleep apnea. Understanding the causes of high blood pressure in men and women is important, as it allows for targeted interventions and lifestyle modifications to prevent or manage this chronic condition.
It is recommended that men and women regularly monitor their blood pressure, make healthy lifestyle choices, and work closely with their healthcare provider to maintain optimal cardiovascular health.
Age or Heredity
While lifestyle factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress can contribute to hypertension, age and heredity also play significant roles. It is important for men and women to be aware of these factors and take proactive steps to maintain optimal blood pressure levels.
Age plays a substantial role in the development of high blood pressure in men and women. As people age, their blood vessels become less flexible, leading to an increase in diastolic pressure. Diastolic pressure is the force exerted on the artery walls between heartbeats. In contrast, systolic pressure, which is the force exerted on the artery walls when the heart contracts, tends to increase with age.
Heredity is another important factor to consider. If one or both of your parents have hypertension, you are at a higher risk of developing the condition yourself. Genetic factors can influence the body’s regulation of blood pressure and contribute to hypertension.
Moreover, younger men are now facing an increasing prevalence of hypertension, which has been attributed to factors such as increased body mass and rising obesity rates. Obesity puts additional strain on the cardiovascular system, leading to an elevation in blood pressure levels.
Understanding these age and hereditary factors is crucial for men and women to take control of their blood pressure.

Diet and Exercise Habits
Diet and exercise habits play a crucial role in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels in men and women. Adopting a nutritious diet and engaging in regular physical activity have been shown to help lower and control blood pressure.
A healthy diet is essential for managing blood pressure. It is recommended to reduce sodium intake, as high sodium levels can increase blood pressure. Additionally, incorporating potassium-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, and low-fat dairy products can help counterbalance the effects of sodium and lower blood pressure.
Maintaining a healthy weight is also important for blood pressure control. Excess weight puts strain on the cardiovascular system, leading to higher blood pressure levels. A balanced diet that includes whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables can support weight management.
In addition to a healthy diet, regular physical activity is crucial for controlling blood pressure. Engaging in aerobic activities such as brisk walking, running, or cycling can help strengthen the heart and improve blood flow. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise each week.
By adopting a healthy diet that limits sodium intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and engaging in regular physical activity, men and women can effectively lower and control their blood pressure levels.
Alcohol Consumption or Smoking
Alcohol consumption and smoking both have detrimental effects on blood pressure in men and women. Excessive alcohol intake can lead to a significant increase in blood pressure levels. It also weakens the heart muscle and contributes to cardiovascular disease, making individuals more susceptible to heart attacks and heart failure.
Similarly, smoking cigarettes also raises blood pressure and damages the artery walls, leading to a higher risk of developing cardiovascular problems. The chemicals in tobacco smoke narrow the blood vessels, reducing blood flow and oxygen supply to the heart and other organs.
To reduce alcohol consumption, it is advisable to limit intake to moderate levels. Men should aim for no more than two standard drinks per day, while women should aim for no more than one. It is also recommended that individuals avoid smoking altogether, as it can have a significant impact on blood pressure and cardiovascular health. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, using nicotine replacement therapy, or joining smoking cessation programs can greatly assist in the quitting process.
Incorporating regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, and managing stress are additional lifestyle changes that can positively impact blood pressure. By making these adjustments and eliminating harmful habits, men and women can greatly reduce their risk of developing hypertension and its related health complications.

Stress and Anxiety Levels
Stress and anxiety levels can have a significant impact on blood pressure in men and women. When we experience stress or anxiety, our bodies release hormones that cause our heart to beat faster and our blood vessels to constrict. This temporary response is often referred to as the “fight-or-flight” response and is a natural part of human survival.
However, chronic stress can lead to a persistent increase in blood pressure, which over time, can contribute to the development of hypertension or high blood pressure. Elevated blood pressure can put a strain on the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
Managing stress levels is crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Various coping mechanisms and activities can help reduce stress and promote relaxation. Regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises or strength training, can release endorphins and help alleviate stress. Engaging in relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation can also have a calming effect on the mind and body.
Other activities that can help reduce stress include listening to calming music, practicing deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy and peace. It is important for men and women to find healthy ways to cope with stress to maintain their blood pressure within a normal range.
Remember, taking care of your mental and emotional well-being is just as important as taking care of your physical health.
How to Lower Your Blood Pressure Naturally
Although medication can be prescribed to manage high blood pressure, there are also natural ways to lower blood pressure. Making certain lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress levels, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can have a positive impact on blood pressure levels.
In addition, maintaining a healthy weight, monitoring sodium intake, limiting caffeine consumption, and practicing relaxation techniques can also contribute to reducing blood pressure naturally. By implementing these strategies, individuals can take control of their blood pressure and improve their overall health and well-being.
Increase Physical Activity Level
Increasing physical activity level is crucial for maintaining and improving overall health, including blood pressure control. Engaging in at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic activity can make a significant difference in blood pressure management.
Activities such as biking, swimming, brisk walking, or wheelchair activities are all excellent options for improving cardiovascular fitness and reducing blood pressure. These types of exercises increase the heart rate, promoting blood flow and strengthening the heart muscle. Regular physical activity also helps to maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or have been sedentary for a long time. A healthcare professional can provide personalised advice on suitable activities and ensure they are done safely, considering your specific needs and limitations.

Make Dietary Changes
Making dietary changes can effectively help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. One of the crucial aspects of a healthy diet for blood pressure management is consuming a low-fat and balanced diet. This involves incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into meals.
One key dietary recommendation for blood pressure control is restricting salt intake. This can be achieved by avoiding processed, packaged, and fast foods, which tend to be high in sodium. Instead, opting for fresh, whole foods and using herbs, spices, and other flavourings to enhance taste can be beneficial.
Another dietary change that can help maintain a healthy blood pressure is cutting back on caffeine. While caffeine does not have a profound and long-lasting effect on blood pressure, it can cause temporary spikes. It is best to be mindful of the amount of caffeine consumed, especially if sensitive to its effects.
Lastly, maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and regular physical activity is essential for blood pressure management. Excess weight can increase the strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to elevated blood pressure levels.
Taking Steps to Reduce Stress
Stress is an unavoidable part of life, and it can have a significant impact on your physical and mental health. Stress can contribute to high blood pressure, so reducing stress levels is an important step in maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Fortunately, there are some simple ways to minimise stress and keep your blood pressure in check.
The first step in reducing stress is to identify the sources of your stress. It may be work, family, relationships, or other external factors. Once the source is identified, it is important to take steps to minimise its impact on your life. This could include setting aside time for self-care activities such as meditation and yoga, or talking to a trusted friend or counsellor about how you are feeling. Additionally, making an effort to get enough sleep and physical activity can also help to reduce stress levels.
Home Blood Pressure Monitoring
Monitoring your blood pressure at home is a great way to keep track of your health and make sure you are staying within a healthy range. Home tests provide much more accurate results than those taken in medical facilities; as the environment can often cause a rise in anxiety which affects readings. With many digital monitors now available to buy, it is even easier to monitor your own health from the comfort of your own home.
Ensuring that every device you use has been properly tested is vital to make sure you get an accurate reading. This is why the British Hypertension Society puts out information regarding validated devices that are available for purchase so people know exactly what they should be using when monitoring their own health. This ensures accuracy and safety when taking blood pressure readings at home. You can find an affordable, approved home blood pressure monitoring machine here.
FAQs
Which blood pressure number is more important?
The most important number when it comes to assessing an individual’s potential for cardiovascular disease is the systolic blood pressure reading (the first number).
Accurately measuring systolic blood pressure is essential for gauging potential risk of heart attack and stroke. It is one of the primary indicators of how serious a person’s condition is as they age and should be checked regularly with healthcare professionals as part of routine medical exams. Therefore, it can be unequivocally concluded that the first number – often referred to as “Systolic Blood Pressure” – holds a significantly more important level of relevance than the second number – diastolic blood pressure – in terms of evaluating potential cardiac risks.
What time of the day is blood pressure highest?
Blood pressure is an important indicator of heart health. It is usually highest in the morning upon waking (known as morning hypertension), due to the body releasing stress hormones such as adrenaline. This increase can be attributed to natural circadian rhythms, as well as starting to move around after lying down for several hours. Also, standing up can cause a temporary bump in blood pressure because gravity causes more blood to flow towards the lower part of the body.
Physical activity, stress and certain medications may also lead to a spike in blood pressure readings. While it is normal for blood pressure levels to fluctuate throughout the day, if it remains consistently high during all times then it may be a sign of long-term hypertension or high blood pressure. Other factors that affect readings include age, size, physical activity and even gender; with men tending to have higher blood pressures than women of the same age group.
Who is at risk of getting high blood pressure?
High blood pressure can increase your risk of serious health conditions such as heart attack or stroke. There are certain lifestyle factors that can increase your chances of getting high blood pressure. Your risk is higher if you have a family history of high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease or diabetes. If you are African American, age 60 or older, have high cholesterol, smoke, drink too much alcohol, or use oral contraceptives (birth control pills), you’re at greater risk for developing high blood pressure.
What blood pressure is too low?
Low blood pressure, also known as hypotension, is defined as a reading below 90/60 mmHg. While it’s not dangerous for people with healthy cardiovascular systems, low blood pressure can cause dizziness, lightheadedness, and fainting in some cases. Low blood pressure may be the result of an underlying medical condition or caused by taking certain medications.
What blood pressure is too high?
Having a high blood pressure is a serious issue that needs to be monitored regularly. High blood pressure is classified as having a reading with a top number of 180 or higher and/or a bottom number of 120 or higher. This is considered to be in the hypertensive crisis range which is dangerously high. If an individual experiences these levels, it is important to seek emergency medical treatment or have someone take them to the hospital for further care immediately.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding normal blood pressure is essential for both men and women in maintaining their overall health and well-being. By knowing the ideal range and taking necessary steps to keep it within that range, individuals can reduce the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases and other related health issues.
Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and appropriate medical interventions when needed are all crucial in maintaining normal blood pressure levels for men and women. Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and being proactive in managing blood pressure can lead to a longer and healthier life.
Please note: This blog post may contain sponsored links, from which we may earn a small commission to support our work at no extra cost to you.